Static Brazilian disk test
The static Brazilian experiments using the electro-mechanical universal testing machine (CRIMS DNS-100) on two types of glasses, test set-up is shown in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 The static Brazilian disk test set-up.
The specimens were diametrically placed between two hard steel platens to avoid necessary indentation from glass particles.
The BD specimens (AG and CSG) were compressed at the constant loading-rate of 0.12 mm/min (2 × 10^-6 m/s).
- annealed glass (AG)
- chemically strengthened glass (CSG)
the cylindrical specimens of Ø 10 mm and height 8
how to modeling this set up

Fig. 1 The static Brazilian disk test set-up.
The specimens were diametrically placed between two hard steel platens to avoid necessary indentation from glass particles.
The BD specimens (AG and CSG) were compressed at the constant loading-rate of 0.12 mm/min (2 × 10^-6 m/s).
- annealed glass (AG)
- chemically strengthened glass (CSG)

the cylindrical specimens of Ø 10 mm and height 8
how to modeling this set up
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!

Comments
I don´t know how to model the faliure of the glass, never had worked with such material.
Could you please explain a little why you would do such analysis/test in glass?
If the material has some load rate dependence, I think you can simply set the properties to what they would be for the load rate you're using. Then do nonlinear static analysis with quasi-static similar to the PipeClip.liml example described in Help -> Manual, or linear analysis with any displacement and just scale the solution to simulate any time in the compression process.
to make a table like that, what should be chosen in the mecway table? because I'm not like that when copying from Mecway.
what options are chosen?
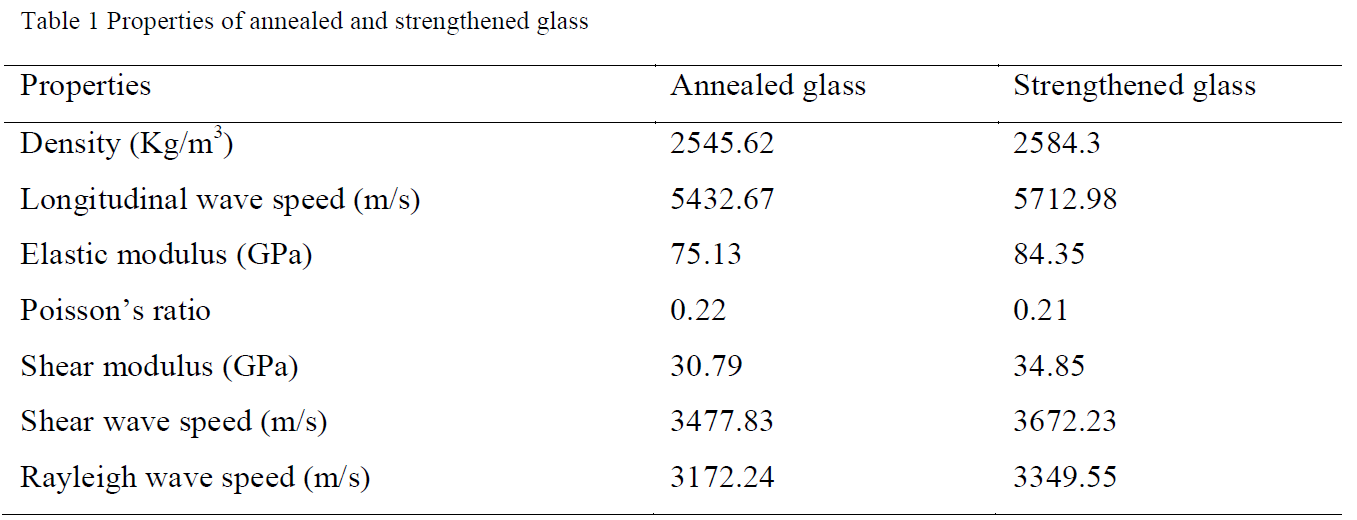
The intent of this research is to determine the tensile strength and fracture behavior of annealed and chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass under static and dynamic loading conditions using Brazilian disc (BD) tests. Owing to high brittleness and very small failure strain of glass, this test method is preferred to indirectly measure the tensile strength by compressive loading of cylindrical specimens diametrically instead of using direct tensile test.
based on experiments obtained curves like the picture below.
*NODE PRINT,NSET=NSET_MOVIL,TOTALS=ONLY
RF
*NODE PRINT,NSET=NSET_PILOT,TOTALS=ONLY
U
Oh, I see